
-
Intel processor graphics GPUs have two main groups of hardware:
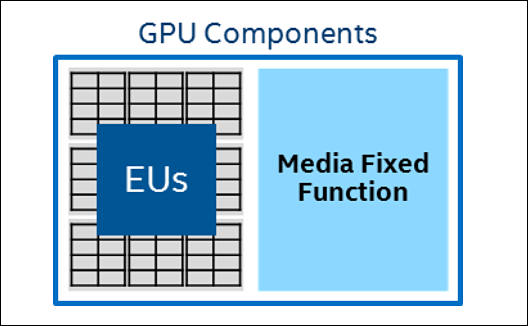
*Execution Units/EUs: General purpose execution units. These are used for graphics rendering, but they are also suited to a wide range of media processing tasks. * Media Fixed Function: In addition, specialized fixed function hardware accelerates video codec and frame processing algorithms for fundamentally higher performance at lower power than the EUs or CPUs.
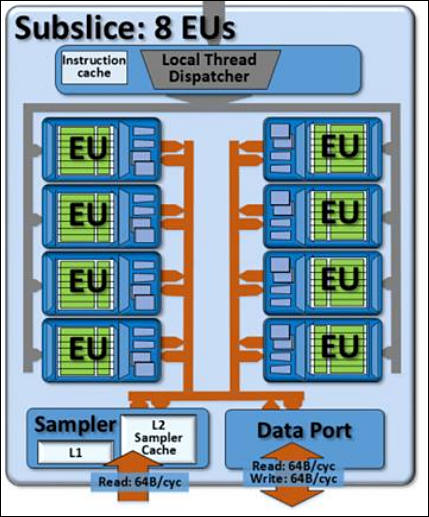
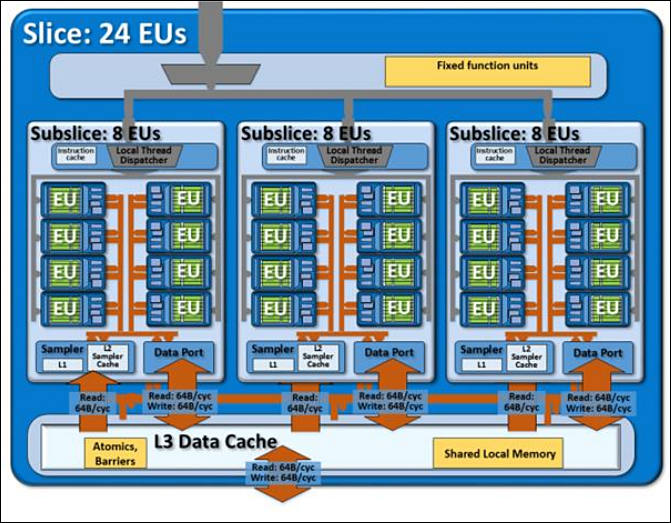
The basic unit of the GPU architecture is the subslice. This contains EUs and memory components. They are assembled into slices.
Subslices are assembled into slices
Execution Units are general purpose compute engines ideal for video processing uses. They are often used by encode for parts of the algorithm not run in fixed function like rate control and mode decisions. The samplers are also highly important to media tasks. They are used by resize and motion estimation.
In addition to EU slices, there is an “unslice” with additional hardware engines individually schedulable for media tasks:

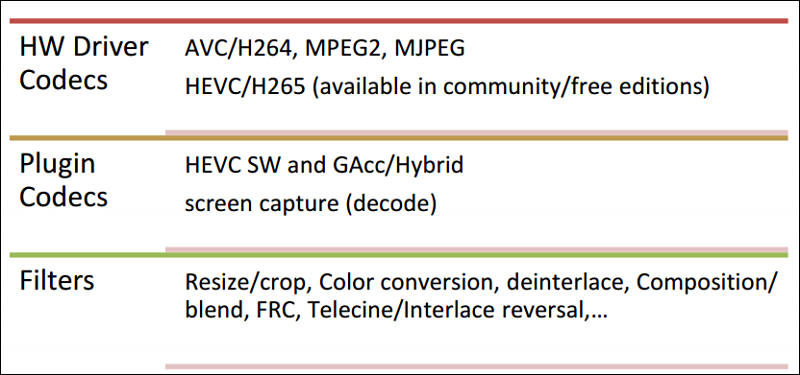
- VDBox (also known as MFX) for codec operations
- VEBox (also known as VQE) provides hardware acceleration for video enhancement/frame processing operations.
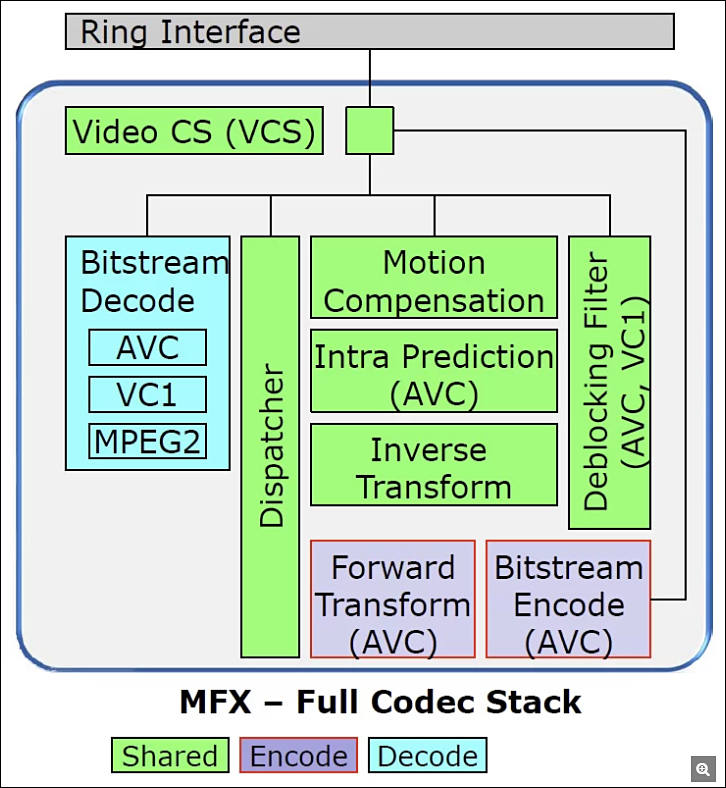
VDbox/MFX contains:
- Bitstream decoder (BSD).
- ENC (intra prediction, motion estimation)
- PAK (quantization, entropy coding, pixel reconstruction, motion compensation)
VEbox/VQE contains:
- Denoise
- Advanced Deinterlace (ADI)
- Local Adaptive Contrast Enhancement (LACE)
- Camera processing features (skin tone enhancement, etc.)
Intel FP32 GPU performance is still very low
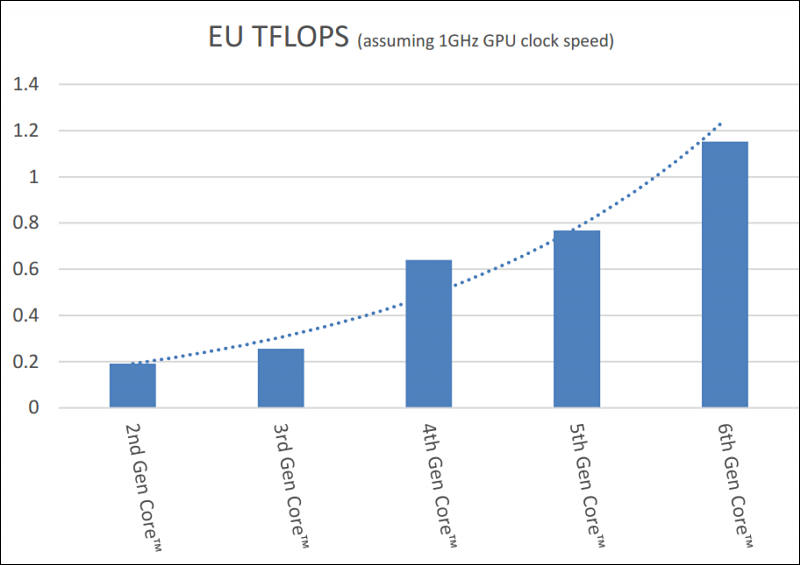
Info from https://software.intel.com/sites/default/files/managed/09/02/Intel_Media_Developers_Guide.pdf
-
7th gen CPUs addition
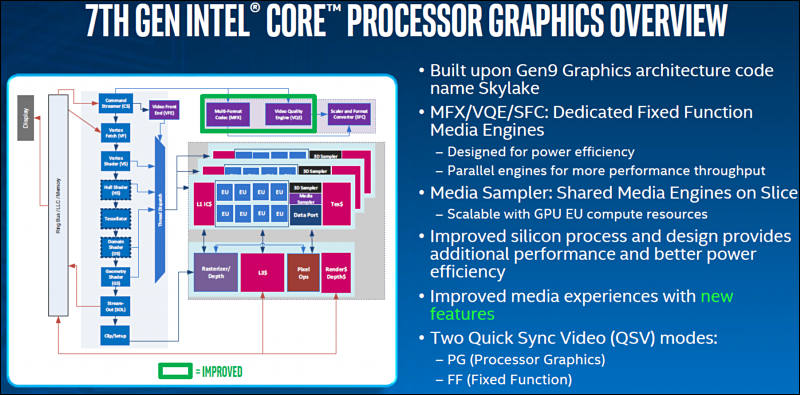
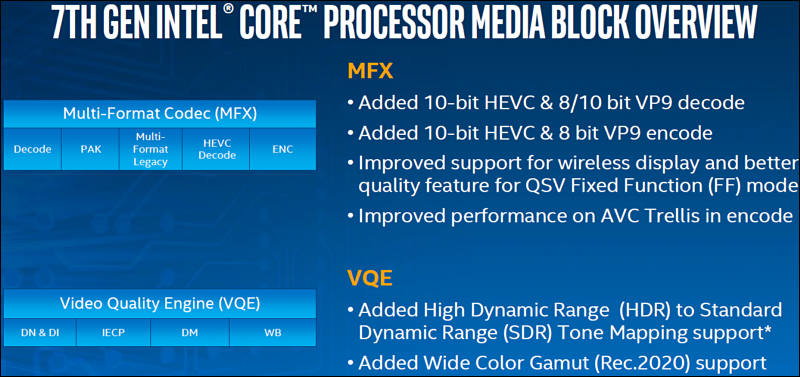
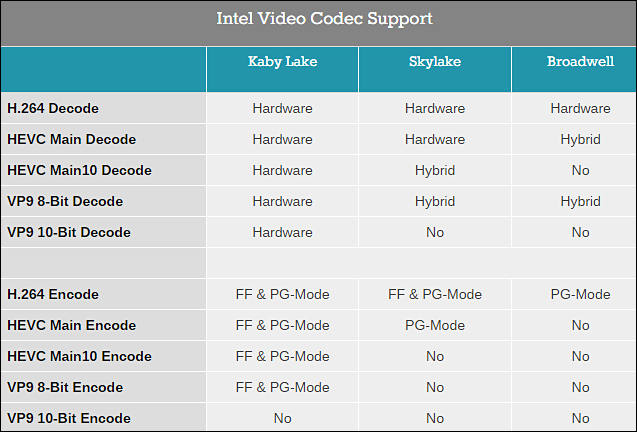
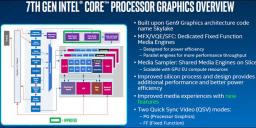
 sample305.jpg800 x 395 - 94K
sample305.jpg800 x 395 - 94K
 sample306.jpg800 x 377 - 78K
sample306.jpg800 x 377 - 78K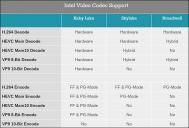
 sample304.jpg637 x 432 - 55K
sample304.jpg637 x 432 - 55K -
Good page about QuickSync, old but good
http://www.tomshardware.com/reviews/ivy-bridge-benchmark-core-i7-3770k,3181-7.html
Note that 3770K already can decode multiple 4K H.264 streams.
 sample546.jpg726 x 788 - 108K
sample546.jpg726 x 788 - 108K
Howdy, Stranger!
It looks like you're new here. If you want to get involved, click one of these buttons!
Categories
- Topics List23,991
- Blog5,725
- General and News1,354
- Hacks and Patches1,153
- ↳ Top Settings33
- ↳ Beginners256
- ↳ Archives402
- ↳ Hacks News and Development56
- Cameras2,367
- ↳ Panasonic995
- ↳ Canon118
- ↳ Sony156
- ↳ Nikon96
- ↳ Pentax and Samsung70
- ↳ Olympus and Fujifilm101
- ↳ Compacts and Camcorders300
- ↳ Smartphones for video97
- ↳ Pro Video Cameras191
- ↳ BlackMagic and other raw cameras116
- Skill1,960
- ↳ Business and distribution66
- ↳ Preparation, scripts and legal38
- ↳ Art149
- ↳ Import, Convert, Exporting291
- ↳ Editors191
- ↳ Effects and stunts115
- ↳ Color grading197
- ↳ Sound and Music280
- ↳ Lighting96
- ↳ Software and storage tips266
- Gear5,420
- ↳ Filters, Adapters, Matte boxes344
- ↳ Lenses1,582
- ↳ Follow focus and gears93
- ↳ Sound499
- ↳ Lighting gear314
- ↳ Camera movement230
- ↳ Gimbals and copters302
- ↳ Rigs and related stuff273
- ↳ Power solutions83
- ↳ Monitors and viewfinders340
- ↳ Tripods and fluid heads139
- ↳ Storage286
- ↳ Computers and studio gear560
- ↳ VR and 3D248
- Showcase1,859
- Marketplace2,834
- Offtopic1,319




