-
For five months of 2021, 755 thousand mortgage loans were issued in the country, which is 44% more than in the same period last year, in monetary terms, the volume of lending amounted to 2.15 trillion rubles. In May alone, the Russians took out 145 thousand loans for 435 billion rubles.
Collapse of this market will be staggering.
-
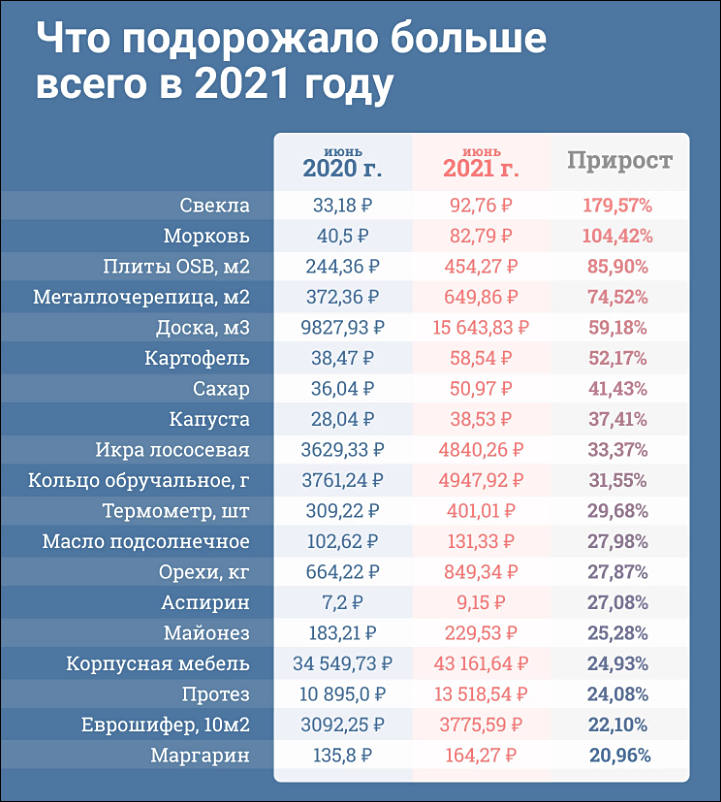
Sugar price
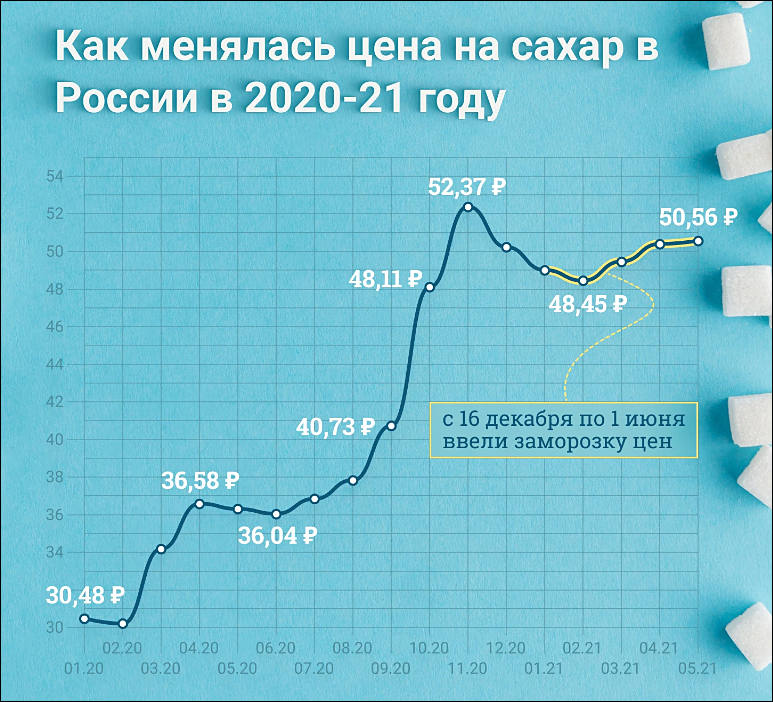
Food inflation

Vegetables prices dynamics
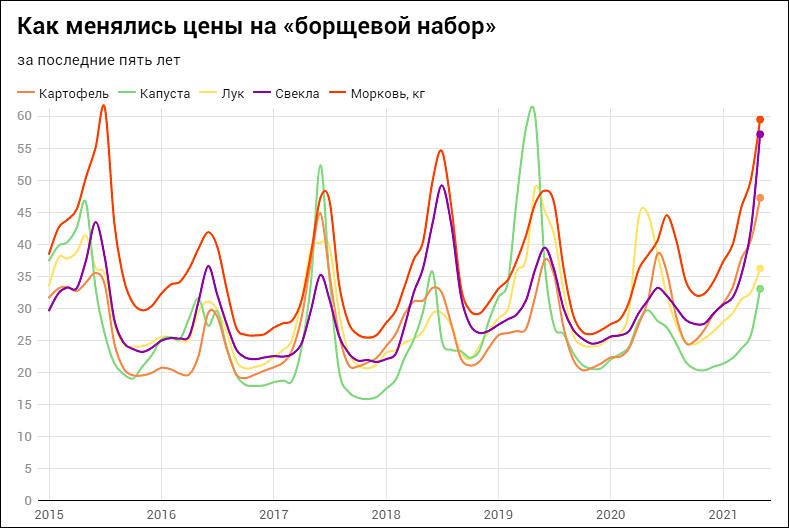
Most fun is that prices always increase artificially in addition to seasons (seasons are especially sharp in capitalist states where they buy something for 10 rub/kg, store for 6 months with expenses around 5-6 rub/kg and sell for 70 rub/kg ), to make potato more expensive large retailers stop to supply Egypt or any similar already expensive foreign potatoes. But stopping allow to start selling inferior product at 200-400% margin. Same is true for lot of other stuff.

 sa17507.jpg773 x 702 - 106K
sa17507.jpg773 x 702 - 106K
 sa17506.jpg755 x 770 - 94K
sa17506.jpg755 x 770 - 94K
 sa17505.jpg789 x 528 - 73K
sa17505.jpg789 x 528 - 73K -
The number of open brokerage accounts by the end of 2021 may reach 15 million, Chairman of the Board of the Moscow Exchange Yuri Denisov. In the long term, all economically active Russians can open an account on the exchange.
Biggest reason is that people want to get government bonds that give higher profit compared to bank deposit.
-
The Russian government has supplemented the list of products that are prohibited from importing from the territory of Ukraine by a decree of December 29, 2018. This was reported on Friday, July 2, on the portal of legal information.
By the decree of June 28, 2021, the list of prohibited products included sugar, pasta, mayonnaise, ketchup, mixed spices, soups and ready-made broths, mineral water, soft drinks, ice cream, muesli and a number of other products.
The import of barley, palm oil, canned meat, crustaceans and molluscs is also prohibited. It is forbidden to import products used for feeding animals, as well as cake.
In addition, the import of various types of timber, boxes, boxes, packing cages, drums, pallets, boxes and other loading boards is limited.
Certainly new price hikes are coming, and local "patriotic" manufacturers and resellers will be able to buy many extra yachts this season, this is for sure.
-
Russians who work only remotely, by July 2021, there were 11%.
Another 6% of respondents reported that they work in a hybrid format - that is, they alternate work from home with an office. 83% said they work offline.
In March 2021, there were three times more people working remotely - 30%. Another 15% worked in a hybrid format.
36% of respondents working remotely, in whole or in part, said that their companies are planning to introduce a hybrid work format. 27% of respondents indicated that employees in their company will continue to work remotely in the future.
More than half (51%) of those who work remotely or may not come to the office said they would like to keep the opportunity to work this way forever.
Huge part of present COVID is due to capitalists and especially mid level management who pushed people into offline mode without any need.
I know at least 2 totally scared managers as in 2020 they discovered that they are not required for work to be going at all most of them time, this is why they tripled number of meetings and 5x increased number of paper work. Now they just turned into parasites.
-
The production of medicines in Russia in physical terms in the first five months of 2021 decreased by 9.2%.
At the same time, analysts note that, in monetary terms, the shipments of drug manufacturers, on the contrary, increased by 25.9% and amounted to 239.1 billion rubles in the first five months.
Just horrible criminals who steal from society and do not care.
-
Everything here is just "perfect":
Salt mining enterprises are faced with a shortage of gondola cars, which may threaten to disrupt supplies.
At the end of March, there were 577.7 thousand open wagons on the railway network, while the market demand was 430-450 thousand units. However, over the past three months, rates for the provision of rolling stock have increased by 40%. Owners and operators have sharply reduced the supply of free parks for loading.
The owners of the wagons guarantee the supply of salt-mining enterprises in quantities that are almost two times less than they need. This has already led to the halt of a number of sites and threatens the fulfillment of obligations to counterparties, up to the disruption of the supply of salt to food enterprises, the appeal says.
A significant increase in rates for gondola cars will lead to an increase in the price of salt for consumers, since logistics takes a significant share in the cost of the product.
Watch how bunch of greedy criminals act.
-
Capital leak from Mordor chart, shows that 2008 even had been aimed at
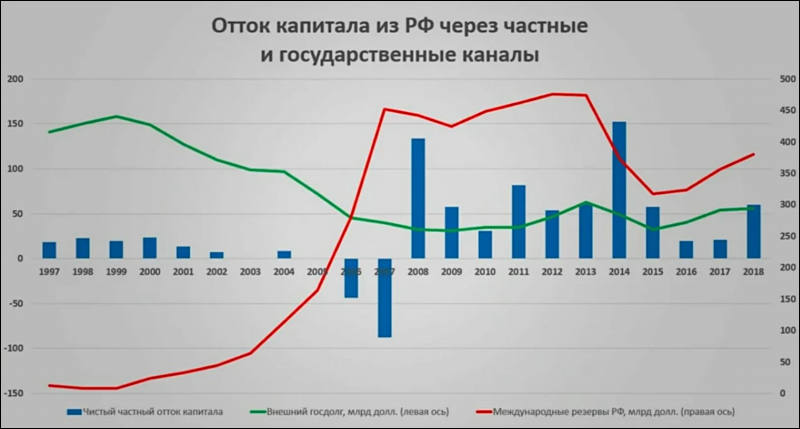
Just numbers are way off, recently it had been independent research made by Netherlands guys who showed that only via offshores and similar channels Russian ruling class returns to owners at least 600 billions USD per year and sometimes it reaches 850 billions USD like in 2020.
Scheme is old and tried, invented by famous Baibakov traitor in 1960x. They sell goods for like $200 per 100 kg, but in reality they get back around $45 per kg, and $155 is being left in the buyer bank, $5-10 of them will be later channeled to clerks and top managers - to their private accounts. All else will remain formally on same account, for infinite amount of time. In reality this money never existed. They just sold goods for 1/4 of price they declared. Normal rates are from 1/3 to 1/2 of real price (oil and metals), sometimes this reach even 70-75% of real price (some food and such). China is using same scheme but it is better looking (you can have your "money" in some government bonds stuff with 30-50 years expiration).

 sa17679.jpg800 x 429 - 40K
sa17679.jpg800 x 429 - 40K -
Over the past 10 years (ie 2010-2019), the Russian economy has grown by 9%. This means that the average annual economic growth rate for this period was less than 0.9%. And this despite the fact that the average annual growth rate of the world economy in the last decade amounted to almost 3%. During these years, Russia demonstrated the worst (with the exception of Venezuela) economic dynamics among the countries of the world with a high share of the raw materials sector in the structure of GDP.
The structure of the population's demand remains extremely primitive. Almost a third of all income Russian citizens spend on food, the level of compulsory payments (debt payments, taxes and fees) is constantly growing.
The share of wages in the structure of product prices has remained stable over the past 15 years, while the quality of jobs and wages are at an extremely low level. The median salary does not exceed 35 thousand rubles. More than 25% of the employed (excluding migrants) work in low-productivity jobs and perform the functions of low-skilled workers. More than 22% of those employed in industrial enterprises are used ineffectively. With such reserves of growth in labor productivity, it is at least strange to talk about a shortage of labor resources. The low level of wages in the existing structure of the Russian economy is becoming the main brake on economic growth and qualitative changes in the social sphere.
Used in 2014-2019. the system of measures of monetary and budgetary policy led to the outstripping growth of prices for raw materials in the domestic market. The tax system has lost its harmony and requires almost constant "manual" adjustment. In the economy, there was a redistribution of resources from producers in favor of the financial sector. Every year in the financial sector (business, government and population) accumulated about 10% of the GDP of "excess" financial resources that did not work for economic growth.
At present, the issues related to the economic (price) availability of energy within the country are quite acute. For the period 2015-2020 it decreased: for gasoline - by 20%, electricity - by 14%, falling back to the indicators of ten years ago. As a result, there is a long stagnation in domestic demand for energy, which limits the growth of the quality of life of Russians.
Assuming that in 2020-2040. the average annual growth rate of labor productivity in the Russian economy will be equal to 1% (for comparison, in 2002-2018 it was equal to 3.2%), the real effective dependency ratio (from all dependents) will be 99.6% in relation to 2018 Thus, in the long term, even relatively low growth rates of labor productivity will be enough to maintain the current level of real demographic burden on the economy.
The average level of capacity utilization in the Russian economy before the 2020 crisis was about 65%. In the extractive industry and export-oriented sectors, the utilization is about 80%. Manufacturing enterprises focused on domestic consumer demand have less than 65%, and about 40% in the investment complex. The share of investments aimed at reconstruction and modernization, since 2008, has decreased from 21% to 15%, the share of completely worn-out equipment, respectively, increased from 13% to 18.7%. Industries focused on the domestic market, the bulk of whose revenues are denominated in rubles, are forced to either reduce investments or purchase cheaper and less efficient equipment.
The inclusion of the Russian economy in the world economy in the early 1990s, the liberalization of foreign economic activity and domestic prices, the rejection of industrial policy led to the fact that Russia's specialization in the supply of hydrocarbons and other primary raw materials has significantly increased. If from 1995 to 2013 the share of hydrocarbons in world exports increased by 10 percent. (mainly under the influence of the outstripping growth in prices for hydrocarbons), in Russia over the same period the share of hydrocarbons in exports increased by 28%. p. (from 43 to 71%). At the same time, the share of high-tech products in Russian exports in 2017 amounted to 2.5% (as in 1995), compared with 20% on average throughout the world. The Russian economy is rather weakly involved in the production chains of the largest countries. For example, in response to an increase in output in the US economy by $ 1,000, direct global demand for Russian products is growing by only $ 3.5, slightly higher than this figure with a similar growth in China - $ 9.8. Even with an increase in production in Germany (Russia's largest trading partner) this figure does not exceed $ 20. This means that in the current model of world distribution of production, Russia receives very modest benefits from the expansion of the world economy and trade.
International comparisons show that income differentiation in Russia is extremely high. Over the past decade, it has only increased, despite the fact that the real level of average income has increased slightly. According to the results of the survey of household budgets of Rosstat in 2018, the average per capita nominal monthly cash income was 23.6 thousand rubles, while in 2008 it was 10.2 thousand rubles. At the same time, the level of consumer prices in 2008-2018. increased by 2.1 times. In real terms, the increase in average per capita money income over this period amounted to only 11.9%, moreover, in 2015-2018. his level has not changed.
The problem is that the growth in real wages observed by statistics is predominantly concentrated in the upper income groups of the population, where the level of needs is relatively saturated - therefore, their expenditures, despite the general decrease, have hardly decreased. This leads to the fact that the income growth of the wealthiest groups of the population is largely transformed into savings or purchases of imported products, which reduces the contribution of consumer demand to GDP growth. The key factor in the intensification of the contribution of consumer demand to the acceleration of economic dynamics is the growth of income and demand of low-income groups of the population.
Bringing the wages of certain categories of workers to the established level was accompanied by a reduction in the number of employees. So, in almost all regions in 2017-2018. the number of junior medical personnel was decreasing, and the reduction in two years is calculated several times. In Moscow, the reduction in this category was 3 times, in the Arkhangelsk region - 3.9 times, in the Perm Territory - 4.5 times, in the Republic of Bashkortostan - more than 5 times. A similar situation has developed with respect to the category of social workers, whose number, for example, in Mordovia has decreased by 6.4 times, while in the Perm Territory this category of workers has practically disappeared. The decline in the number of employed people was accompanied by an increase in their workload.
Domestic R&D expenditures in Russia are at a very low level - for many years they have been about 1.1 - 1.2% of GDP. At the same time, in China, these costs amount to 2.1% of GDP, in the USA - 2.7%, in Germany - 2.9%, and in the leading countries (Israel, South Korea) they exceed 4% of GDP.
Spending on education is also well below the levels of developed countries. In general, education currently spends about 4.3% of GDP, which significantly lags behind the values of 2009 (5.7% of GDP). At the same time, the OECD countries spend on average more than 6% of GDP for these purposes, and the leading countries - more than 7% of GDP (Finland, Great Britain, Sweden, Israel, Indonesia).
At present, the average salary of doctors in Russia (in terms of PPP) is more than 5 times lower than the salary of medical specialists in Germany and the Netherlands, 4.7 times lower than in Great Britain, 3.5 times - than in Finland. The implementation of measures of national and federal projects will ensure an increase in the salaries of doctors (according to PPP) in relation to the level of 2018 to 119.3% in 2024 and 138% in 2035. At the same time, the gap with Western countries will decrease insignificantly - in 2035 The salaries of doctors in Russia will be 3.8 times lower than the current level of salaries for specialists in Germany.
-
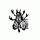
How much of real causes of Morder revolutions, 1905 and 1917, do they teach in Morder schools? Or in elite private schools for that matter? In the US education system, such topics are generally forbidden and so people who are poor, sick, in debt and overworked, just think it is their fault and rich people 'just worked harder'. And when things get worse they fall for nonsense conspiracies which give much more convenient reasons for hard times.
-
Well, now it is capitalism, so all school history books are proper ones. I mean, that they can list some real reasons and real facts, but all else is turned such way that people are being told lies.
Why do yo think we have huge pro czars procession each year? As only totally uneducated and brainwashed people can even think about participating in such.
-
As much as 90 per cent of recorded sanitary logging in the country is "pseudo-sanitary", or carried out on false or questionable pretexts. This is supported by studies such as one by WWF in 2019, which found that 96 per cent of the planned sanitary felling sites it examined had been allocated improperly.
It is a big red flag, then, that Irkutsk oblast regularly produces more timber through sanitary felling than anywhere else in Russia. The province has a high-profile history of abusing these rules, and those charged with enforcing them a long history of turning a blind eye. In 2019, Irkutsk's top forestry official, Sergey Sheverda, was arrested for facilitating the illegal felling on false sanitary grounds of woodland in a nature reserve.
Long report on how Ikea is using illegal and criminal wood.
-
The Accounts Chamber published a report on the results of the audit of the effectiveness of the management of the state subsoil fund for 2018-2020 with disappointing conclusions. Over the past three years, Russia has imported more than a third of strategic minerals and over 60% of scarce minerals. For a number of names, in particular, for manganese, chromium, titanium and lithium, Russian needs are fully covered exclusively by imports, and for zirconium this figure is 87.2%.
First - any research and making new mines is "unprofitable".
Second - most of rich sources of minerals are now on exUSSR territories.
-
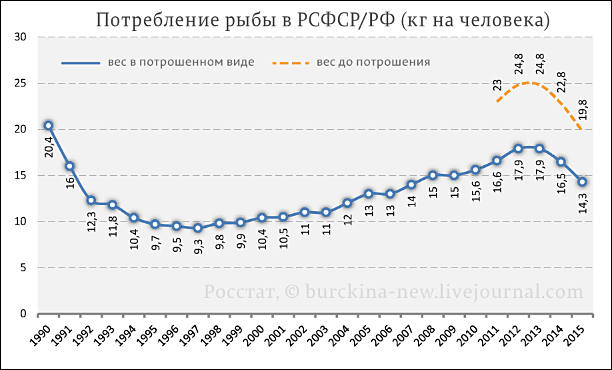
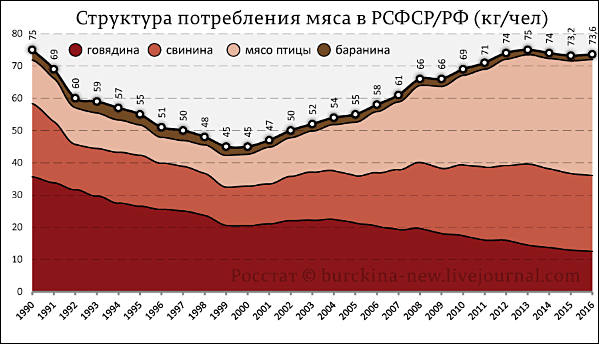
Fish consumption
Meat consumption

 sa17790.jpg612 x 370 - 40K
sa17790.jpg612 x 370 - 40K
 sa17791.jpg599 x 344 - 43K
sa17791.jpg599 x 344 - 43K -
Russia has become the only country that has complied with the Paris Agreements, having actually reduced CO2 emissions from 3.1 billion tons in 1990 to 1.6 billion tons of CO2 in 2017, i.e. by 48%.
All the reduction went to making EU life better. As it is exactly oil, wood, coal and gas that they got for almost free.
-
Carrot price chart
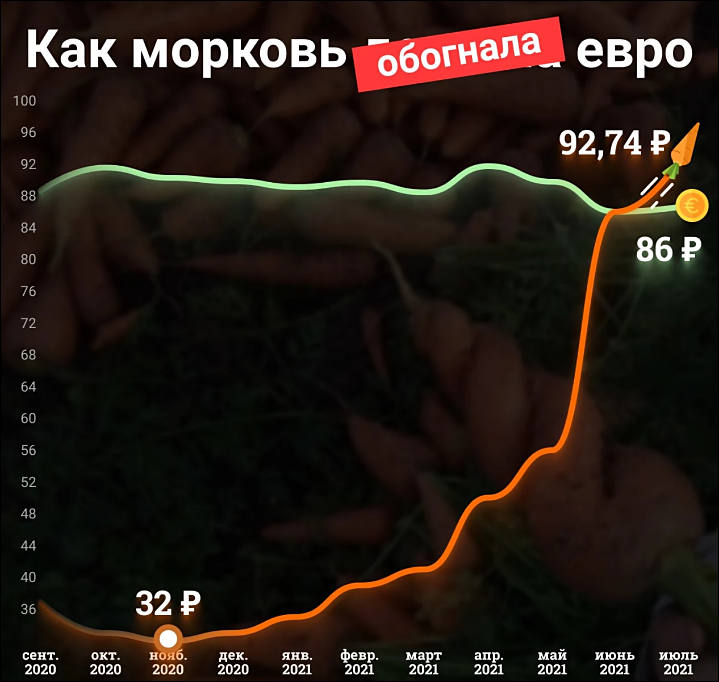
Note that all huge profits go to the pockets of huge trade and logistics monopolies.
People who grow carrots can get 10-15% from final price until they are also big agro holding owned by oligarchy.
 sa17821.jpg719 x 682 - 59K
sa17821.jpg719 x 682 - 59K -
To keep exports of resources and energy government reduced number of new build homes
And since June almost all personal homes projects are also stopped due to 200-300% inflation on materials.
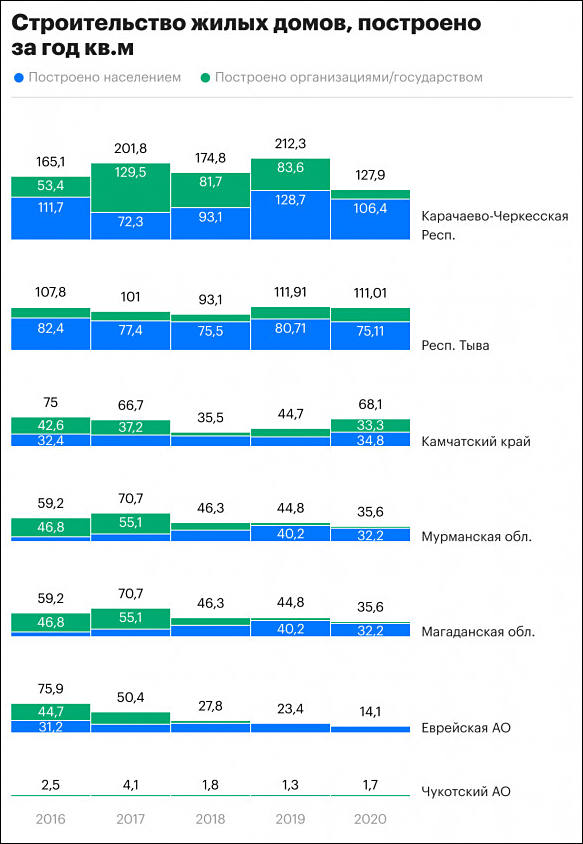

 sa17856.jpg583 x 844 - 75K
sa17856.jpg583 x 844 - 75K -
The combined wealth of the richest Mordor oligarchs has grown by almost $ 40 billion since the beginning of the year.
Top gains:
- The main owner of Severstal, Alexei Mordashov: plus $ 6.14 billion since the beginning of the year, total fortune - $ 29.2 billion, 51st place in the general list of billionaires;
- The head of NOVATEK Leonid Mikhelson: plus $ 5.82 billion since the beginning of the year, total fortune - $ 30.6 billion, 47th place;
- The main owner of NLMK, Vladimir Lisin: plus $ 5.48 billion since the beginning of the year, total fortune - $ 29.3 billion, 50th place;
- Member of the board of directors of NOVATEK and Sibur Gennady Timchenko: plus $ 4.52 billion since the beginning of the year, total fortune - $ 21.2 billion, 89th place;
- LUKOIL President Vagit Alekperov: plus $ 4.01 billion since the beginning of the year, total fortune - $ 21.3 billion, 87th place;
- President and co-owner of Norilsk Nickel Vladimir Potanin: plus $ 3.36 billion since the beginning of the year, total fortune - $ 33.4 billion, 42nd place;
- The largest shareholder of USM Holdings Alisher Usmanov: plus $ 3.11 billion since the beginning of the year, total fortune - $ 21.1 billion, 91st place.
-
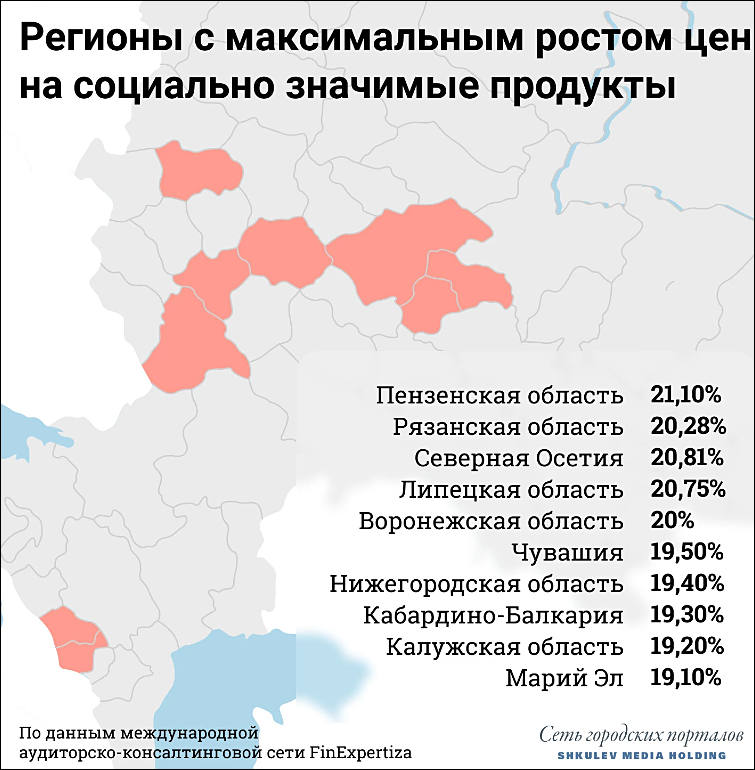
The real disposable income of Russians, calculated in kilograms of potatoes, fell by 26.6% over the year. In the first half of 2021, citizens could purchase 1,232 kilograms of potatoes with an average monthly salary, which is almost 450 kilograms less than in the same period last year, according to a study by the international audit and consulting company FinExpertiza.
It is also noted that the most significant decrease in the purchasing power in terms of potatoes was observed in the Kaliningrad region - by 53.9%, or 1.04 tons of potatoes.
The Altai Republic took the second place in the rating - 44.8%, or 565 kilograms.
The third is the Kostroma region - by 44%, or 568 kilograms.
-
The Association of Confectionery Industry "Askond" announced an increase in prices for domestic transportation by 10-15%, for international it is 24-160%.
Director of the Potato Union Aleksey Krasilnikov said that in a number of directions there is an increase in the cost of transportation by at least 20-30% compared to last year, and in some cases - twice due to the lack of transport and drivers from the CIS countries.
-
Gasoline continues to rise in price in Russia. Since the beginning of 2021, fuel prices of the AI-92 and AI-95 brands, popular among taxi drivers, have grown by 16%, and since 2020, the growth has been more than 20%.
Over the same period, maintenance costs for cars in general increased by almost 15%, and taxis in particular, by almost 20%.
-
The number of Russians with active loans from microfinance organizations (MFOs) has increased by 2.26 million people, or 23.5%, since the beginning of the year, according to statistics from the largest self-regulatory organization on the market, MiR (RBC has data). At the end of the second quarter, there were 11.87 million MFI borrowers in the country. Over the entire pandemic 2020, the base of active clients in this segment grew by 9.5%, or by 835 thousand people.
According to Rosstat, in the second quarter of 2021, the workforce in Russia reached 75.3 million people, that is, MFO borrowers account for 15.8% of the economically active population.
-
The Russian edition of Forbes magazine has published a rating of the richest family clans. In total, the list includes 10 families. Their combined fortune grew by $ 16.1 billion to $ 42.9 billion.
For the first time, the list was headed by the family of the richest woman in Russia, Tatyana Bakalchuk. According to Forbes, the Wildberries company, of which Bakalchuk is the general director, was immediately built as a family-owned company, but formally all 100% belonged to Tatiana. Only on December 31, 2019, she handed over to her husband Vladislav a share of 1%, which made it possible to include their family in the rating. The magazine estimates the total fortune of the Bakalchuk family at more than $ 13 billion.
Howdy, Stranger!
It looks like you're new here. If you want to get involved, click one of these buttons!
Categories
- Topics List23,990
- Blog5,725
- General and News1,353
- Hacks and Patches1,153
- ↳ Top Settings33
- ↳ Beginners256
- ↳ Archives402
- ↳ Hacks News and Development56
- Cameras2,367
- ↳ Panasonic995
- ↳ Canon118
- ↳ Sony156
- ↳ Nikon96
- ↳ Pentax and Samsung70
- ↳ Olympus and Fujifilm101
- ↳ Compacts and Camcorders300
- ↳ Smartphones for video97
- ↳ Pro Video Cameras191
- ↳ BlackMagic and other raw cameras116
- Skill1,960
- ↳ Business and distribution66
- ↳ Preparation, scripts and legal38
- ↳ Art149
- ↳ Import, Convert, Exporting291
- ↳ Editors191
- ↳ Effects and stunts115
- ↳ Color grading197
- ↳ Sound and Music280
- ↳ Lighting96
- ↳ Software and storage tips266
- Gear5,420
- ↳ Filters, Adapters, Matte boxes344
- ↳ Lenses1,582
- ↳ Follow focus and gears93
- ↳ Sound499
- ↳ Lighting gear314
- ↳ Camera movement230
- ↳ Gimbals and copters302
- ↳ Rigs and related stuff273
- ↳ Power solutions83
- ↳ Monitors and viewfinders340
- ↳ Tripods and fluid heads139
- ↳ Storage286
- ↳ Computers and studio gear560
- ↳ VR and 3D248
- Showcase1,859
- Marketplace2,834
- Offtopic1,319